Introduction
In today's interconnected world, a butterfly flapping its wings in the United States (US) can create an economic tornado in India. Well, maybe not literally, but when it comes to the US Federal Reserve's (Fed) monetary policy decisions, the impact on emerging markets like India is quite profound.
Picture this: the Fed, in its quest to tame inflation and steer the US economy, decides to adjust interest rates. Suddenly, it's as if someone has thrown a pebble into the global economic pond, and the ripples start spreading far and wide. These ripples, in the form of changing interest rates, foreign investment flows, and currency fluctuations, reach the shores of India, setting off a chain reaction that influences every corner of the Indian economy.
Now, here's the thing - this economic tango between the US and India has only grown more intense in recent years. It's like the global economy has become one big dance floor, and everyone's moves are more closely synchronised than ever before. When the Covid-19 pandemic hit, central banks around the world, including the Fed, pulled out all the stops to keep their economies afloat. Interest rates skyrocketed, and inflation became the talk of the town.
Fast forward to 2024, and while some central banks have started to ease off the interest rate pedal, others, such as India, are still holding steady. It's a delicate balancing act - trying to keep inflation in check while also ensuring that borrowing costs don't stifle economic growth. And amidst all this, the Fed's actions continue to play a significant role in shaping India's economic trajectory.
In this blog post, we will explore how the Fed's policy actions on interest rates, liquidity measures, and policy guidance influence Indian monetary policy and various aspects of the Indian economy, and what it means for investors, businesses, and policymakers.
The Fed's Global Influence
The Federal Reserve, the central banking system of the US, wields immense influence over global financial conditions through its monetary policy decisions, particularly changes to the federal funds rate. When the Fed adjusts interest rates, it creates a chain reaction that impacts currency valuations, capital flows, and economic activity worldwide.
India, like other emerging markets, is particularly sensitive to these policy shifts. Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI) flows to India tend to slow down or reverse during periods of US monetary tightening. The Indian economy's rapid growth, coupled with its increasing integration into global markets, has amplified its vulnerability to external shocks emanating from advanced economies such as the United States.
Recommended for you
Readers also explored

Balancing Slowdowns and Sectoral Strength

World GDP Breakdown 2025: Who Powers the Global Economy?
Transmission Channels: How the Fed Impacts India
The Fed's policy decisions affect India through several key transmission channels:
Exchange Rate Dynamics: Fed rate hikes typically strengthen the US dollar, potentially weakening the Indian rupee. A weaker rupee can fuel imported inflation and widen India's current account deficit. Research indicates that a 5% depreciation in the rupee against the US dollar can increase India's retail inflation by 20 basis points.
Capital Flows: Higher US interest rates can redirect global capital flows, as investors chase higher yields in US assets. This can lead to capital outflows from emerging markets such as India, tightening domestic financial conditions. Just to get a sense of it, FPI outflows from India began when the Fed started hinting at an interest rate hike in October 2021, resulting in a net outflow of $20 billion in FY2022, which continued in FY2023 but limited to $5.5 billion, as RBI also raised repo rates. With RBI maintaining high interest rates in FY2024, FPI net inflows surged to US$ 41.6 billion. However, since the beginning of FY2025, FPIs have turned net sellers in the domestic market with net outflows of US$ 3.5 billion (till May 31), in anticipation of a delay in interest rate cut by the Fed.
Trade Linkages: A strong US economy, supported by appropriate Fed policy, can boost demand for Indian exports. However, if Fed tightening slows US growth, it could dent external demand for Indian goods and services. The US is one of India's top trading partners, with bilateral trade reaching $118.3 billion in FY2024, with exports amounting to $77.5 billion.
Global Commodity Prices: US monetary policy can influence global commodity prices, particularly oil. As a major oil importer, India is sensitive to these price fluctuations, which can affect domestic inflation and fiscal balance. India imported $179.6 billion of crude oil and petroleum products in FY2024, accounting for nearly 27% of its total imports.
Implications for the Indian Economy
The interplay of these transmission channels can have far-reaching implications for various facets of the Indian economy:
The Interest Rate Tango: Fed Rates and Indian Monetary Policy
When the US Federal Reserve adjusts its policy rates, the RBI often follows suit to maintain the interest rate differential and prevent excessive volatility in currency and financial markets. This correlation has grown stronger in recent years, with the RBI closely monitoring global monetary policy trends while considering India's unique economic conditions and priorities.
The implications of this interest rate tango are manifold. When the Fed hikes rates, it often leads to a corresponding increase in Indian interest rates, affecting borrowing costs for home loans, personal loans, and vehicle loans. Conversely, when the Fed cuts rates, it increases the likelihood of the RBI following suit, potentially making borrowing cheaper and stimulating consumption and investment. While, savers may see their deposit rates decline, resulting in reduced savings income.
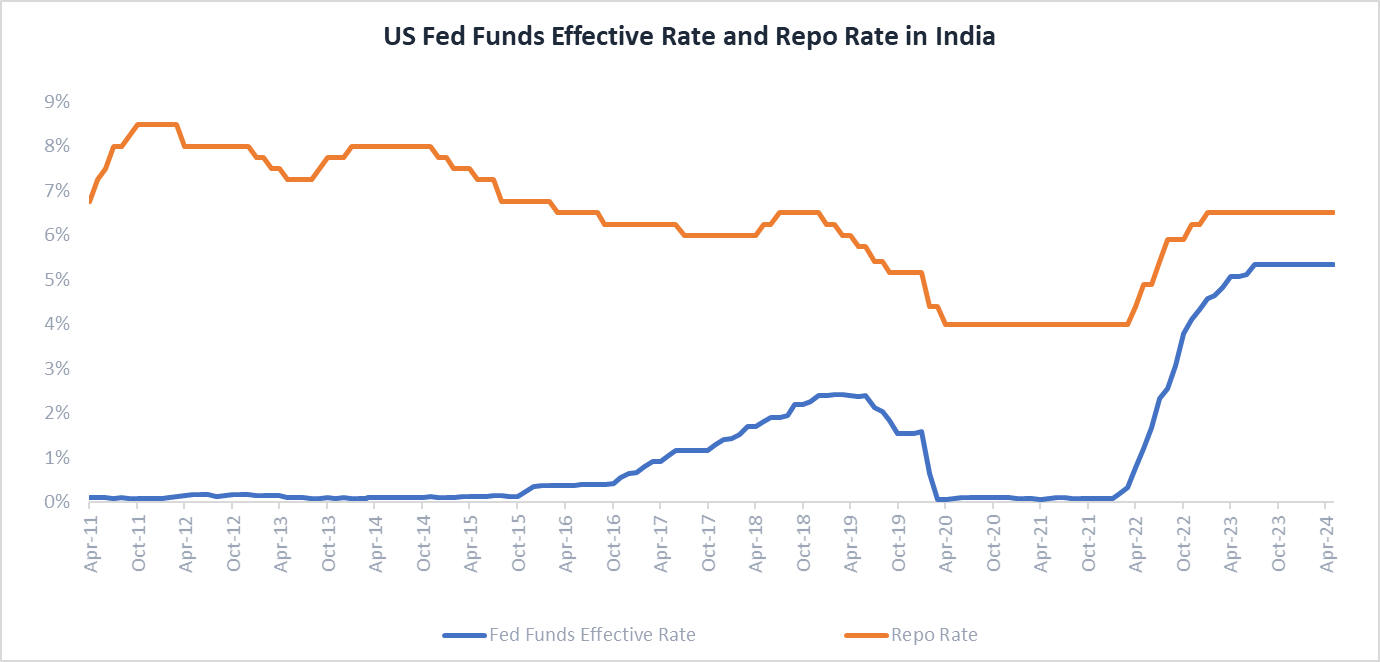
Note: The daily Effective Federal Funds Rate (EFFR) is a volume-weighted median of transaction-level data collected from depository institutions in the Report of Selected Money Market Rates
Financial Markets and Asset Prices
Indian equity and bond markets are sensitive to shifts in global risk sentiment and capital flows. Fed policy decisions can trigger volatility in domestic financial markets, as foreign investors reassess their emerging market exposures. Sectors with significant foreign investment or external linkages, such as IT and pharmaceuticals may be particularly vulnerable to these swings.
External Sector Dynamics
Fed policy can influence India's external balances through its impact on the rupee, trade flows, and capital account dynamics. A widening current account deficit, driven by higher oil prices or weaker exports, can put pressure on the rupee and necessitate policy adjustments.
India's current account deficit narrowed to 0.65% of GDP in FY2024, down from 2.00% in FY2023, partly due to a lower merchandise trade deficit. Managing this deficit sustainably requires a judicious mix of monetary, fiscal, and structural policies.
Economic Growth and Stability
The cumulative impact of Fed tightening on domestic financial conditions, inflation, and external demand can affect India's growth trajectory. While India's domestic demand-driven growth model provides some insulation, prolonged external headwinds can still dampen economic activity.
Empirical evidence suggests that a 100 basis point increase in the US federal funds rate can shave off 0.8% of GDP in emerging economies after three years. Policymakers will need to carefully balance the objectives of supporting growth, containing inflation, and preserving financial stability in the face of evolving global conditions.
Strategies for Resilience Amidst Global Uncertainty
Although the RBI has some policy flexibility, it cannot entirely insulate the domestic economy from global forces. Investors and businesses must stay attuned to these dynamics and adapt their strategies accordingly.
Policymakers: Balancing Stability and Growth
- Strengthen domestic drivers of growth: The government should continue to focus on structural reforms, infrastructure development, and enhancing the ease of doing business to bolster India's domestic growth engines.
- Diversify external economic linkages: Policymakers should actively pursue strategic economic partnerships and trade agreements with a diverse set of countries to reduce overreliance on any single economy. India has recently signed Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) with various nations, especially the Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) with the UAE in February 2022, which is expected to further accelerate cross-border trade and investment flows between the two countries.
- Maintain robust foreign exchange reserves: India should continue to build and maintain adequate foreign exchange reserves as a buffer against external shocks and to inspire confidence in the country's ability to manage its external finances. As of June 28, 2024, India's foreign exchange reserves stood at $652 billion, providing a strong cushion against global volatility.
Businesses: Building Competitiveness and Resilience
- Diversify revenue streams: Companies should explore opportunities to diversify their revenue bases across domestic and international markets to mitigate the impact of external demand shocks. India received its highest annual FDI inflow of $84.8 billion in FY2022, indicating the attractiveness of the Indian market for foreign investors. However, in subsequent years it has come down and reached $70.9 billion in FY2024, partly due to the global slowdown and the scrapping of Bilateral Investment Treaties (BITs) by India.
- Implement robust risk management strategies: Businesses should develop comprehensive risk management frameworks, particularly for managing currency and commodity price risks. This can help mitigate the impact of exchange rate fluctuations and global commodity price volatility on their operations and profitability.
- Invest in innovation and productivity: Firms should prioritise investments in research and development, technology adoption, and human capital to enhance their competitiveness and resilience in the face of global challenges. India's thriving technology ecosystem is well-positioned to benefit from the accelerating global digital transformation.
- Leverage domestic demand potential: Businesses should tap into India's large and growing domestic consumer base, which can provide a stable source of demand and help offset external vulnerabilities. India's unique demographic advantage, its largely young population, sets it apart from other economies and presents significant opportunities for businesses catering to domestic consumption.
Investors: Traversing Uncertainty with a Strategic Approach
- Maintain a well-diversified portfolio: Investors should ensure their portfolios are well-diversified across asset classes, sectors, and geographies to mitigate the impact of external shocks and capture a broader set of opportunities. Diversification can help reduce the overall risk of an investment portfolio and provide a more stable return profile over the long term.
- Focus on quality and resilience: Investors should prioritise companies with strong fundamentals, robust balance sheets, and resilient business models that can withstand global economic uncertainties. Such companies are better positioned to navigate challenges and emerge stronger in the face of external headwinds.
- Adopt a long-term perspective: While short-term volatility can be unsettling, investors should maintain a long-term perspective and avoid knee-jerk reactions to transient market movements. By focusing on their long-term financial goals and staying invested through market cycles, investors can benefit from the power of compounding and the potential for long-term wealth creation.
- Seek professional advice: Given the complexity of global economic linkages, investors should consider seeking the guidance of professional financial advisors to manage the challenges and opportunities presented by evolving global conditions. Experienced advisors can provide valuable insights, help develop tailored investment strategies, and ensure that investment decisions align with an individual's risk profile and financial objectives.
Conclusion
The impact of US Federal Reserve policy on India underscores the complex interconnections of the global economy. While external headwinds pose challenges, India's economic fundamentals, policy flexibility, and entrepreneurial dynamism provide a strong foundation for managing uncertainty.
By staying attuned to global economic developments, embracing innovation, and fostering resilience, Indian stakeholders can not only weather the impact of Fed actions but also seize the opportunities that emerge in a rapidly evolving landscape. In an increasingly interconnected world, staying informed and adaptive is key to financial success and economic resilience.










